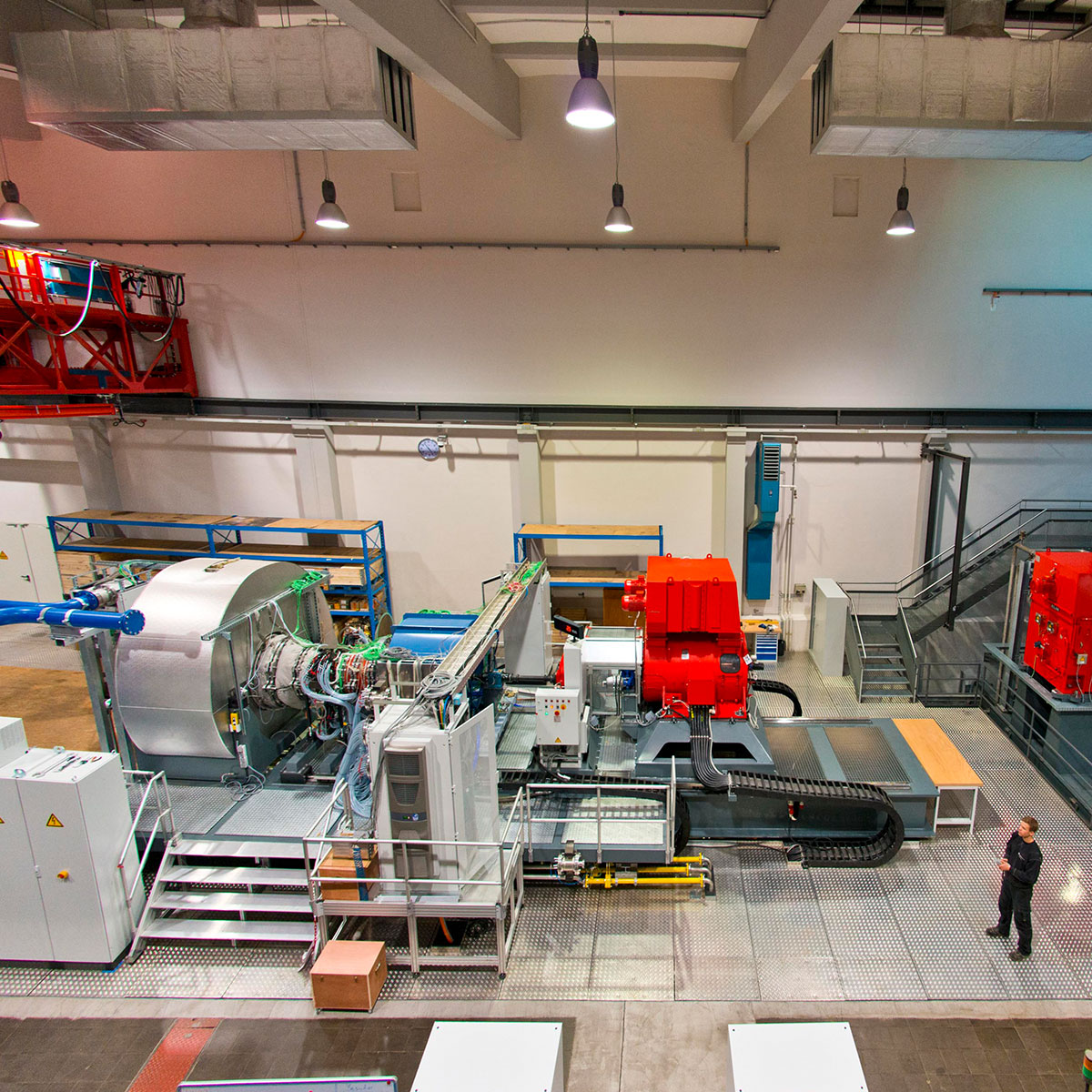
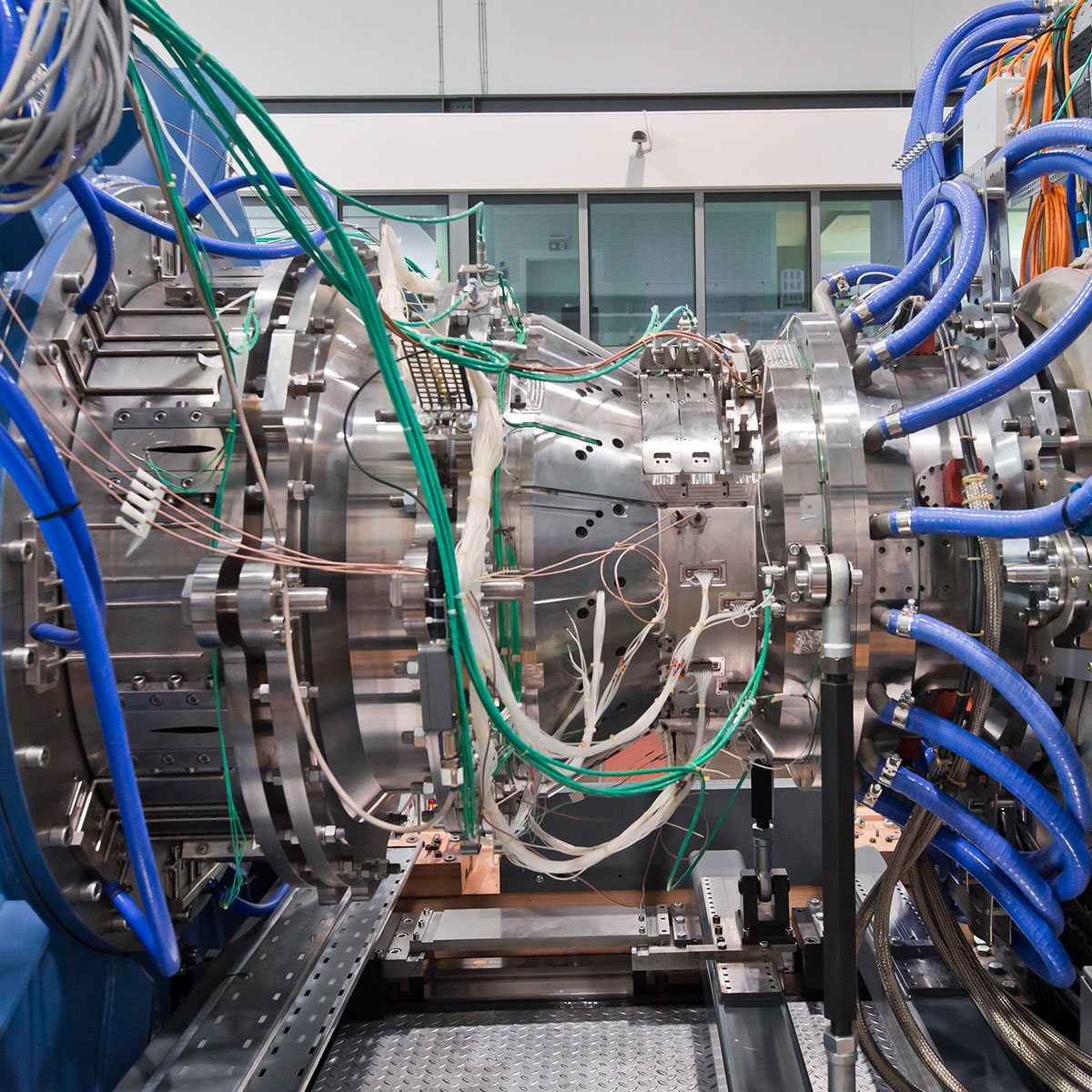
Turbine Test
What is a turbine test?
- Test turbine component for aircraft engines or industrial gas turbines as part of a development programme
- Establish complete turbine operating characteristics under realistic Re-number conditions
- Investigate influence of cooling flow on turbine performance for HP turbines
- Detailed flow investigations
- Provide data base for improvement of the numerical algorithms
Turbine tests are for cost reasons usually performed as so called “cold flow” tests where the turbine inlet temperature is by a factor of 5-6 lower than in a real gas turbine. Therefore the turbine test rig needs to be scaled carefully to simulate the realistic Re-number range during testing.
Keyfacts
Turbine tests are carried out at certified test facilities with partner organisations as well as at the customer site.
We have gained particular experience within the turbine test facilities of the Institute of Aircraft Propulsion Systems (ILA) at the University of Stuttgart and at the German Aerospace Centre (DLR) in Göttingen.
Technical data of ILA Stuttgart facility
- Air supply up to 140 kg/s
- Inlet air conditions -60 °C to 170 °C, inlet pressure 0,05 bis 2,5 bar
- Max. shaft break power 10 000 kW
- Conditioning of cooling water 160 m³/h at 3.5 bar, max. Tin 50 °C / min. T-out 10 °C (e.g. for water brake)
- Oil system 2 x 15l/min and 1 x 10l/min at a maximum of 8 bar and the maximum flow temperature of 70 °C (e.g. for test vehicle)
- Secondary air supply system 2.6 kg/s @ 6 bar and 4.6 kg/s @ 22 bar
- Air dehumidification in the main air supply up to a dew point of at least 7 °C
Technical data of DLR Göttingen facility
- Air supply up to 10 kg/s
- Inlet air conditions 20 °C to 320 °C, inlet pressure 0,1 bis 2,0 bar
- Max. shaft break power 1,5 MW (HDT) and 1,0 MW (NDT)
- Rig oil system, secondary air supply system
We will accommodate individual customer-specific test requirements with the installation and supply of external additional units, such as air dehumidifiers, power generators, heaters, water coolers and apparatus for mass flow and pressure control in secondary air supplies.